Israeli politician and general Ariel Sharon died on January 11, 2014 after being in a permanent vegetative state for eight years. He was born on February 26, 1928. He was the 11th Prime Minister of Israel.
26 February 1928: Ariel Sharon is born at Kfar Malal, 15 miles north-east of Tel Aviv, a moshav (collective settlement) in central Palestine. His parents, Samuel and Vera Scheinerman, had arrived six years earlier from Russia.
1948: Becomes commander in Israeli army from its inception, participating in the war of independence.
1953: Prime minister David Ben-Gurion chooses 24-year-old Sharon to head new elite commando squad called Unit 101.
October 1953: Sharon’s commandos attack Qibya in Jordan and kill 69 residents, including women and children. Many historians feel the raid contributed to the Suez crisis three years later.
1956: Brigade led by Sharon captures strategic Mitla Pass during Suez war. Later criticised for disobeying orders and recklessly endangering soldiers’ lives during operation
June 1967: Major-General Sharon retakes Mitla Pass and Abu Agheila during six-day war
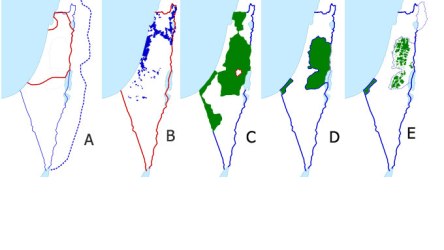
1970-71: Crushes dissent in occupied Gaza by relocating 160,000 refugees, killing 100 Palestine Liberation Organisation suspects, and arresting another 700.
October 1973: Called back to active duty for Yom Kippur war. Claims he turned tide of war by crossing the Suez canal, trapping the Egyptian 3rd army and winning the largest tank battle since Kursk in 1943. Relieved of duty in February 1974.
December 1973: Becomes Knesset member for capitalist Liberal party.
1975: Appointed security adviser to Labour prime minister Yitzhak Rabin.
1977: Forms Shlomtzion political party, which wins two seats in 1977 elections. Merges party with Likud, and becomes minister of agriculture.
1981: Appointed minister of defence after narrow Likud win in elections, and starts planning to alter regional map.
June 1982: Launches Operation Peace for Galilee, later known as the first Lebanon war.
February 1983: Resigns as minister of defence and forbidden from holding post again after being found personally responsible for deaths of 800 and 3,500 Palestinians respectively in Sabra and Shatila refugee camps in Beirut. The killings led to some labelling Sharon as ‘the butcher of Beirut’.
1983: Appointed minister without portfolio. Remains in successive governments, holding a variety of posts.
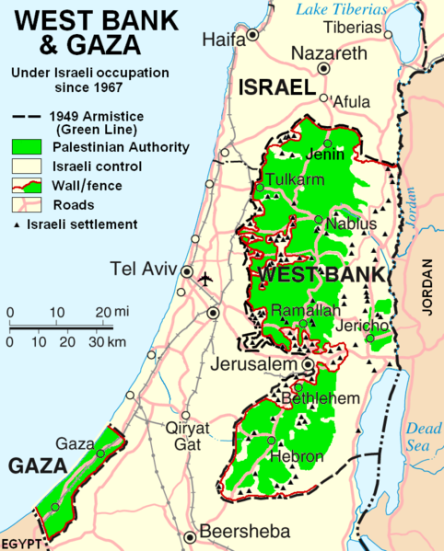
October 1998: As newly appointed foreign minister, astounds acolytes by signing the Wye River agreement, which granted Palestinians control over another 13% of the West Bank.
May 1999: Netanyahu loses national elections. Sharon assumes party leadership and becomes head of opposition.
September 2000: Visits Jerusalem’s Temple Mount with “message of peace” and 1,000 armed police, prompting Palestinian uprising.
February 2001: Comfortably defeats Labour incumbent Ehud Barak in Israel’s last direct prime ministerial elections.
2002: Suicide bombings prompt Sharon to reoccupy Palestinian cities.
January 2003: Likud party wins a resounding victory in elections for the Knesset, and Sharon is returned as prime minister.
April 2003: America releases “roadmap to peace”, which Sharon accepts, despite some objections. He commits Israel to withdraw from West Bank cities and release more Palestinian prisoners.
February 2004: Sharon says Israel will pull out troops from Gaza and evacuate all 22 settlements in the strip, but Likud party members reject plan in May.
February 2005: Speaking alongside Mahmoud Abbas at summit, declares truce in four-intifada.
August 2005: Dismantles all Jewish settlements in Gaza amid fierce protests. Decision dismays Israeli right, who feel he has betrayed the Greater Land of Israel cause.
November 2005: Resigns from Likud and dissolves parliament to create new centrist party from scratch called Kadima (“forward” in Hebrew).
18 December 2005: Rushed to hospital after suffering stroke. Discharged after two days with surgery to repair a small hole in his heart scheduled for early January.
4 January 2006: Suffers another stroke and collapses in bathroom. Operated on for seven hours at Hadassah hospital on edge of Jerusalem, but never regains consciousness.
March 2006: Kadima – with Ehud Olmert as leader – sweeps aside Labour and Likud in elections.
14 April 2006: Declared “permanently incapacitated”, having been in a coma for 100 days. Olmert confirmed as prime minister.
January 2013: Doctors say “significant” brain activity detected during tests on Sharon’s brain, but chances of him regaining consciousness still near zero.
2 January 2014: Sharon’s doctors report that he has suffered multiple organ failure and is clinging to life.
11 January 2014: Sharon dies at Sheba Medical Centre, the long-term care facility near Tel Aviv where he has lain since May 2006.